Intercept 5 – Community Corrections
Proper training to support individuals with mental health and substance use challenges is vital as they continue to navigate their communities and community corrections.
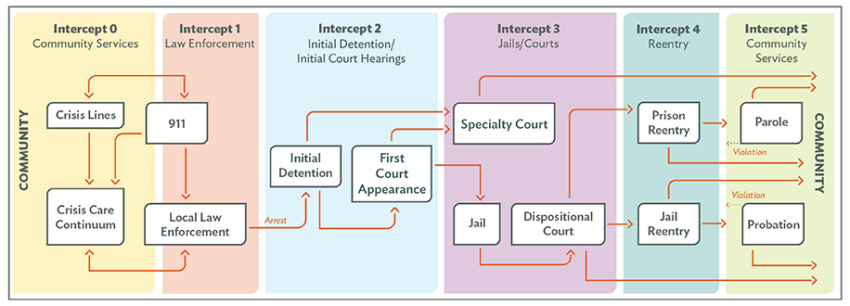
Intercept 5 – Community Corrections
Intercept 5 occurs post-release and usually involves probation or parole or some other correctional supervision. Understanding the impact that mental health and substance use challenges can have on this already stressful transition and ensuring proper, person-centered supports are in place is essential to facilitating the best outcomes possible and sustaining recovery. A key component of intercept 5 is also creating and sustaining community partnerships with these supports.
Intercept 5 CCBHC Integration Opportunities
- Specialized community supervision caseloads of people with MH needs
- Medication-assisted treatment for people with SUDs
- Access to recovery supports, benefits, housing and competitive employment
The extent of CCBHCs’ relationships with community supervision has not been fully documented, but at least 5% of CCBHCs include corrections staff such as external probation and parole offers on treatment teams to create a plan to support successful outcomes for individuals with MH/SU needs. CCBHCs must ensure Medication Assisted Treatment (MAT) and MH medications are part of individuals’ treatment plans where necessary. The majority (89%) of CCBHCs offer direct access to MAT (with the remainder partnering with other organizations to deliver this service), compared with only 56% of SU treatment facilities nationwide. CCBHCs create community partnerships with organizations that provide job training, housing and other needed supports within their communities.
Intercept 5 Core Competencies
Collaboration and Teamwork
- Adopt a single system-wide county definition of key terms consistently used by local behavioral health systems, jails, courts and community corrections, including but not limited to:
- Substance use disorders
- Serious mental illness
- Recidivism
- Conduct a Sequential Intercept Model mapping workshop.
- Identify service capacity/interventions/gaps.
- Understand respective roles and responsibilities.
- Obtain leadership commitment (criminal justice council or task force).
- Develop collaborative criminal justice and behavioral task force if one does not already exist.
Workforce Development
- Identify evidence-based interventions and best practices for improving the jail-to-treatment pipeline:
- MAT (Long Acting Injectables)
- Trauma Informed Care (TIC)
- Motivational Interviewing
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Housing services
- Family support
- Vocational training
- Literacy training
- Employment assistance
- Peer Navigators/Recovery Coaches
- Provide cross-systems training on:
- Substance Use Disorder and MAT
- Implicit bias
- Data and evaluation
- Trauma-informed Care
- MHFA for public safety
- Motivational Interviewing
- Screening, Brief Intervention and Referral to Treatment (SBIRT)
- Peer Navigators/Recovery Coaches
- Integrated mental health treatment for co-occurring substance use disorders
Screening and Assessment
- Assess the individual’s clinical and social needs and public safety risk.
- Implement validated screening and assessment tools and an efficient screening and assessment process.
- Inclusive of social determinants screenings and assessments
- Utilize the Risk, Needs, Responsivity (RNR) Model and ensure alignment with behavioral health treatment approach.
- Criminogenic risk
- Substance use/misuse
- Mental illness
- Share assessment information with partners to streamline workflow and coordinate care.
Care Planning and Care Coordination
- Utilize the Assess, Plan, Identify and Coordinate (APIC) Model to coordinate reentry services.
- Develop process for linking to services (warm handoffs).
- Plan for the treatment and services required to address the individual’s needs, both in custody and upon reentry.
- Inclusive of in-reach services related to Medicaid suspension/enrollment
- Identify required community and correctional programs responsible for post-release services.
- Coordinate the transition plan to ensure implementation and avoid gaps in care with community-based services.
- Guidelines for Successful Transition of People with Mental or Substance Use Disorders from Jail and Prison: Implementation Guide
- Data Collection Across the Sequential Intercept Model (SIM): Essential Measures
Cultural Humility
- Apply and address across remaining categories once competent in these principles:
- Implement/enhance anti-racist training and education.
- Adapt services to language, gender and pronoun preferences and cultural norms of population served.
- Develop task force that is inclusive of individuals with lived experience to spearhead the implementation/assessment of anti-racist policies and procedures, training and education.
Racial and Ethnic Disparities
- Identify and address racial disparities within criminal justice system involvement and in health care access and quality for populations served.
- Develop task force for racial and ethnic disparities to help achieve the following goals:
- Set qualitative process and outcome goals for racial and ethnic disparity reduction.
- Set a numerical target for reducing justice system involvement and/or improving outcomes for Black, Indigenous and people of color (BIPOC).
- Set a numerical target for reducing the relative likelihood of justice system involvement for BIPOC compared to White adults.
Evaluation and Quality Improvement
- Develop a city/county-level training plan that includes quality assurance to ensure fidelity.
- Develop a city/county-level plan for information/data sharing.
- Data Collection Across the Sequential Intercept Model (SIM): Essential Measures
- Agree on how to measure recidivism and other health outcomes. For example:
- Recidivism outcomes:
- Reduction in police contact, arrest and reincarceration.
- Health outcomes:
- Reduction in wait time for accessing services.
- Track no-shows.
- Track medication refills.
- Rate of homelessness upon release/access to housing.
- Reduction in hospitalization/ER rates.
- Increase access to care coordination.
- Reduction in wait time for Medicaid reinstatement.
- Recidivism outcomes:
Funding and Sustainability
- Prioritize policy, practice and funding improvements.
- Understand Medicaid/SSA coverage.
- Routinely communicate with the people responsible for the county budget.
- Utilize data to justify funding.
- Explore federal funding opportunities.
National Council Resources
- 2021 CCBHC and Justice Systems Report
- 2022 CCBHC Impact Report
- Addressing Health Equity and Racial Justice Resource Directory
- Health Equity Resource Directory
- Trauma-informed, Recovery-oriented Systems of Care Toolkit
- The Intersection of Criminal Justice, Race and Addiction: The Case of Harold Easter
- Fostering Resilience and Recovery: A Change Package
- Tools for Overdose Prevention
- Care Pathways Toolkit
- COVID-19 Pandemic Impact on Harm Reduction Services: An Environmental Scan
- Oral Health, Mental Health and Substance Use Treatment Toolkit
- Overdose Prevention and Response in Community Corrections Environmental Scan
- Overdose Prevention and Response in Community Corrections Courses
Want to Learn More?
- Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration (SAMHSA): Assess, Plan, Identify, Coordinate (APIC) Implementation Guide
- SAMHSA: Principles of Community-based Behavioral Health Services for Justice-involved Individuals: A Research-based Guide
Relias Online Courses
Click here to access a wide variety of on-demand courses to enhance your care.
